The CBT Triangle: How Behaviors Influence Your Recovery



As a Clinical Research Specialist, writer, and person with lived experience in mental health recovery, Grace blends clinical research with honest storytelling to inspire healing and hope. In her free time, she enjoys writing books for young adults, an age when she needed stories the most.

Dr. Mala, is the Chief Clinical Officer at Recovery.com, where she develops impartial and informative resources for people seeking addiction and mental health treatment.




As a Clinical Research Specialist, writer, and person with lived experience in mental health recovery, Grace blends clinical research with honest storytelling to inspire healing and hope. In her free time, she enjoys writing books for young adults, an age when she needed stories the most.

Dr. Mala, is the Chief Clinical Officer at Recovery.com, where she develops impartial and informative resources for people seeking addiction and mental health treatment.
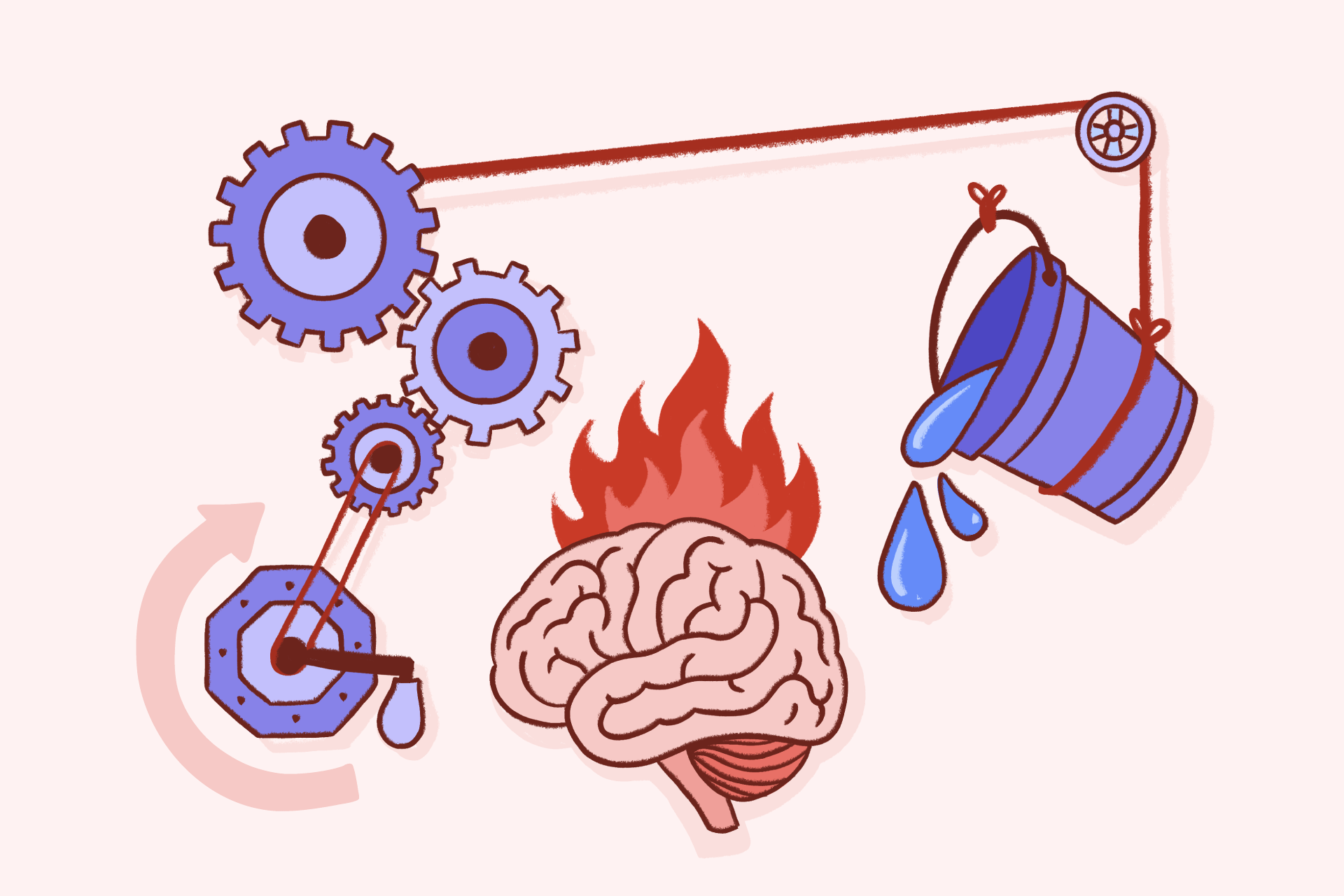
The cognitive behavioral therapy (CBT) triangle uses the interconnected nature of emotions, thoughts, and behaviors to positively change thoughts and mood, primarily through behaviors.
According to the CBT triangle, you have the majority control of your behaviors and actions.1 You have some control of your thoughts. And you have zero control over your emotions. So you can’t control how you feel, but you can control how you think and behave.
Leveraging this has been revolutionary for many people in treatment, and long-term recovery.
Leveraging The CBT Triangle
Since the 3 elements of emotions, thoughts, and behaviors feed into each other, the CBT triangle posits changing your behaviors (which you have the most control over) will change your thoughts and emotions.2 Similarly, changing your thoughts can also positively affect your emotions and behaviors.
For example, someone experiencing depression may think, “I can’t get out of bed. I’m too depressed.” This could lead to emotions of helplessness and self-hatred.
Getting out of bed proves your control of what you do, even if you don’t feel like doing it. Realizing your abilities can lead to more positive emotions and helpful thoughts. You may even be encouraged to tackle another difficult task…creating a snowball effect.
As you get more practice, you’ll likely become more aware of unhelpful thoughts AND how you act on them. As awareness grows, you’ll have more opportunities to correct untrue thoughts or act opposite to your thoughts and feelings.
The CBT triangle helps with multiple conditions, too.3 These include depression, anxiety, obsessive compulsive disorder (OCD), addiction recovery, and trauma.
Behavioral Activation: Valued, Routine, and Enjoyable Activities
Behavioral activation (BA) centers on doing something even if you don’t feel like it, not waiting for motivation or to “feel better”—and in doing so, you can actually feel better.4 Scheduling activities or doing them as-needed can offer symptom relief by breaking the negative emotions-thoughts-behavior pattern of depression.
There are 3 types of BAs. Here they are in detail.
Valued BAs
Your valued BAs include activities related to what, where, or who you value. Your values are like north stars, guiding you through life. They might include spirituality, family, creative expression, friendship, and more.
Doing a valued BA could look like practicing a religion, spending purposeful time with family, engaging in social settings with friends, and creating art.
Symptoms of depression or other illnesses can make valued activities harder to do. Intentionally doing them, like attending church even if you don’t want to, can add value back into your life.
Enjoyable BAs
Enjoyable BAs are things you like to do. They bring you pleasure and add joy to your life. Examples could include cooking, painting, sports, hobbies, outings with friends, and eating good food.
One of the symptoms of depression is struggling to feel pleasure, even if it’s something you used to love.5 Reincorporating enjoyable BAs can help you regain interest and pleasure in these activities.
Routine BAs
Your routine BAs include day-to-day tasks you must manage to stay healthy, employed, housed, and more. They may not be particularly enjoyable, but they’re important for maintaining a fruitful life.
Routine activities include paying bills, going to work, doing laundry, brushing your teeth, showering, doing schoolwork, and tidying up.
BAs and The CBT Triangle
Conditions like depression, trauma, and addiction can push many BAs off to the wayside, affecting your thoughts and emotions. You may not feel pleasure from your enjoyable BAs, and your symptoms could get in the way of routine and valued activities. Engaging in BAs can change your thoughts and emotions for the better, ending the cycle of negative effects.
By starting with what you have the most control over, behaviors, you can change your thoughts and emotions and stop the cycle of negative thoughts/unhelpful behaviors.
For example, you may have emotions of sadness and thoughts of worthlessness because you can’t get anything done. But you exercise control of your behavior and get up and do the dishes, even though you don’t want to. This action challenges your thoughts of worthlessness and can change your sad emotions into neutral or encouraged ones.
The CBT Triangle and Recovery Maintenance
When you use the connections of the CBT triangle to improve your mood by changing your thoughts and behaviors, you’ll likely notice your success isn’t infinite. Reaping continuous benefits from the CBT triangle takes repetition and practice. The more you do it, the easier it will be to keep doing it—like any other habit.
Once you feel you’re in the maintenance phase of your recovery, you can leverage the CBT triangle differently. Instead of using it to address symptoms, you can start using it to prevent symptoms.
For example, maybe you’ve learned to manage your depression symptoms. You know your warning signs and have a good grasp on what situations will trigger a negative mood or spiraling thoughts. You also know not going into the office makes you feel lonely and more isolated. When you start feeling like isolating, you proactively address this symptom by going to the office. Since you’re going in and not isolating, your feelings of loneliness don’t get the chance to fester and worsen to the point of redeveloping depression.
Leveraging the CBT triangle isn’t just a tool for depression, either. You can use it for substance use recovery, behavioral addictions, anxiety, and other emotions that aren’t serving you. Its benefits can be life-long.
For more intensive treatment options, use Recovery.com to find rehabs and outpatient clinics focused on depression recovery.
FAQs
-
Nakao, Mutsuhiro, et al. “Cognitive–Behavioral Therapy for Management of Mental Health and Stress-Related Disorders: Recent Advances in Techniques and Technologies.” BioPsychoSocial Medicine, vol. 15, Oct. 2021, p. 16. PubMed Central, https://doi.org/10.1186/s13030-021-00219-w.
-
Profits, Think. “How to Use the Cognitive Triangle.” AANMC, 7 Mar. 2024, https://aanmc.org/naturopathic-medicine/cognitive-triangle-cbt/.
-
“In Brief: Cognitive Behavioral Therapy (CBT).” InformedHealth.Org [Internet], Institute for Quality and Efficiency in Health Care (IQWiG), 2022. www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov, https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK279297/.
-
Behavioral Activation for Depression. University of Michigan, https://medicine.umich.edu/sites/default/files/content/downloads/Behavioral-Activation-for-Depression.pdf.
-
Depressive Disorder (Depression). https://www.who.int/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/depression. Accessed 7 Feb. 2025.
Our Promise
How Is Recovery.com Different?
We believe everyone deserves access to accurate, unbiased information about mental health and recovery. That’s why we have a comprehensive set of treatment providers and don't charge for inclusion. Any center that meets our criteria can list for free. We do not and have never accepted fees for referring someone to a particular center. Providers who advertise with us must be verified by our Research Team and we clearly mark their status as advertisers.
Our goal is to help you choose the best path for your recovery. That begins with information you can trust.